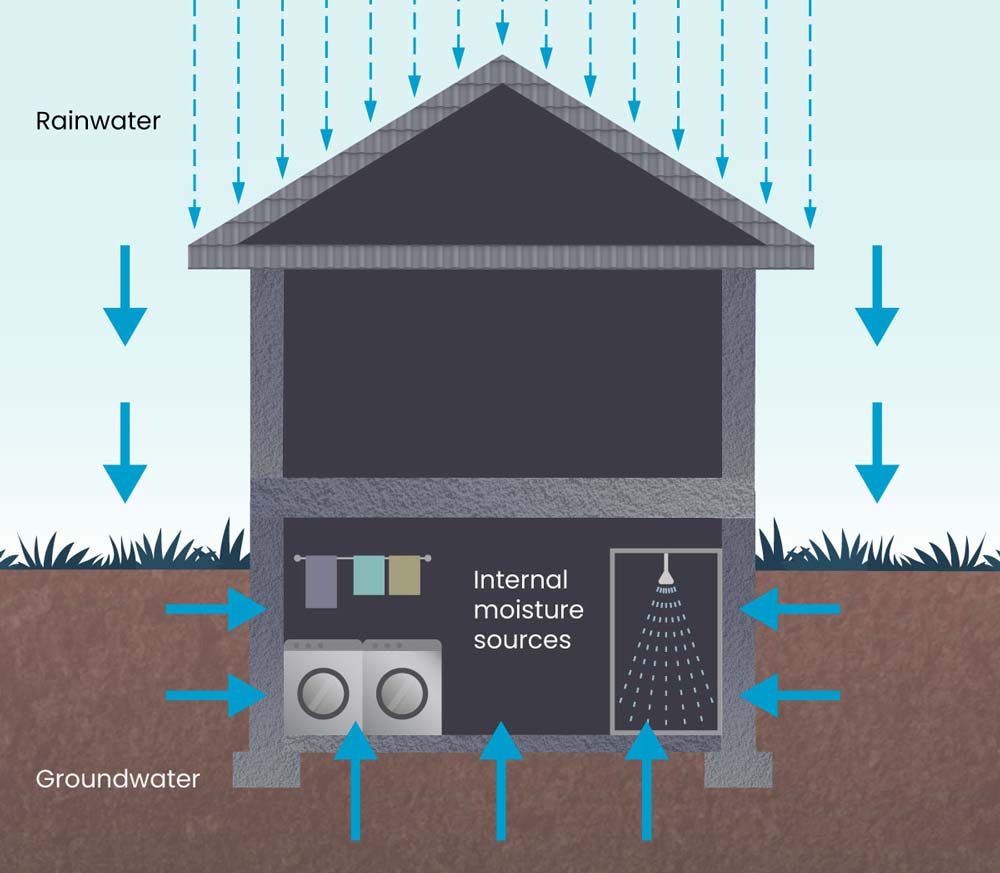
Basement moisture comes from leaks, ground water, and indoor air condensation.
If you want a dry, healthy home, you need to understand what causes moisture in basement. I have inspected hundreds of basements, from brand-new builds to century homes. In this guide, I break down the science and the fixes in plain English, so you can find the source fast and stop it for good.
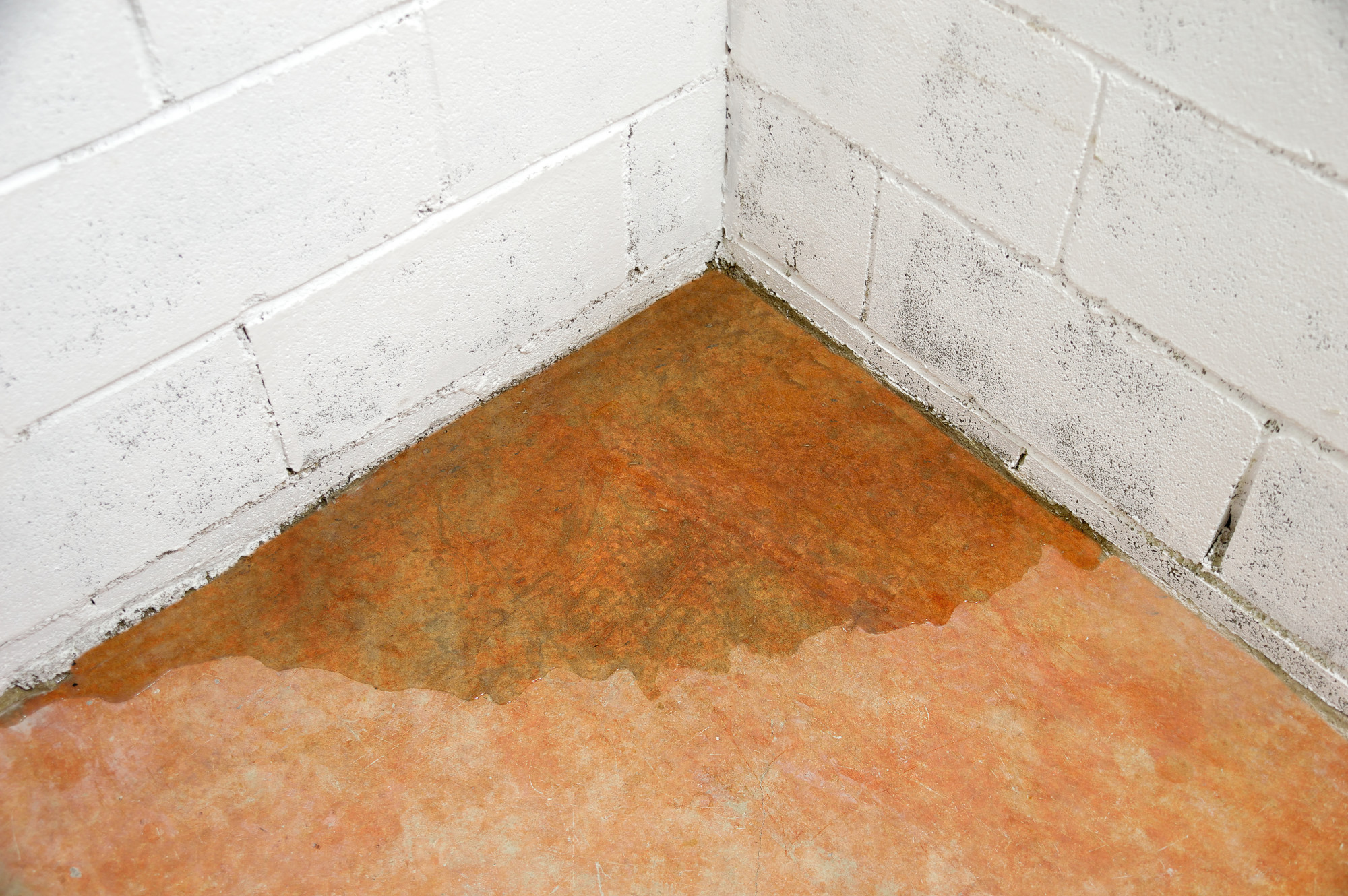

How moisture enters a basement: the core causes
Most problems trace back to water that moves as liquid or vapor, or to air that cools below its dew point. Here is a clear look at what causes moisture in basement and how each source behaves.
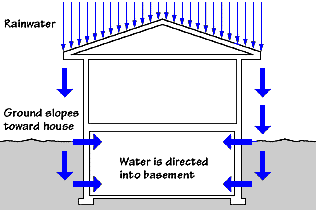
- Surface water against walls. Poor grading, short downspouts, and clogged gutters dump rain right at the foundation. Water then seeps through cracks and joints.
- Rising damp from soil. Concrete is porous. Water can wick in from wet soil and the footing if there is no capillary break.
- Hydrostatic pressure. A high water table pushes water through tiny gaps. Even hairline cracks can leak under pressure.
- Condensation on cool surfaces. Warm humid air meets cool walls, ducts, or pipes. Water drops out of the air and wets surfaces.
- Vapor diffusion. Moisture in soil moves as vapor through concrete slabs and walls. It raises indoor relative humidity.
- Window wells and entry points. Bad well drains, missing covers, or failed seals let water collect and spill in.
- Plumbing and HVAC leaks. Drips from supply lines, drains, water heaters, or AC coils add to the load.
- Sump or drain tile failures. No pump, bad pump, power loss, or a clogged interior drain leads to backup.
I often see two or more causes at once. That is why a quick mop-up does not last. Solve the source first, then control the air. This is the best way to tackle what causes moisture in basement.
Source: therealsealllc.com
Spotting the problem: signs, tests, and diagnosis
Your nose and eyes are great tools. Then use a few simple tests to confirm what causes moisture in basement before you spend money.
Common signs
- Musty smell. Often the first clue that humidity stays high.
- Efflorescence. White powder on walls shows water moved through and left salts.
- Peeling paint or bubbling. Trap moisture and it will push paint off.
- Rust and rot. Metal rusts and wood softens when wet.
- Dark spots or damp carpet. Check corners, cold joints, and around posts.
- Mold on baseboards or behind storage. Low air flow zones grow mold first.
- Spalling concrete. Freeze and salt can pop the surface of damp walls.
Simple tests I use
- Plastic sheet test. Tape a 2-foot square of clear plastic to a wall or slab. If water beads under the plastic, moisture is coming through the concrete. If it beads on top, indoor air is condensing.
- Hygrometer check. Place a digital temperature and humidity sensor in the space. Aim for 45 to 55 percent RH in cool seasons.
- Infrared scan. On a hot humid day, cold wet zones show as cool spots on thermal images.
- Tape compass test on floor. Lay a cheap compass on the slab and watch for needle drift near cracks. Air leaks often form at gaps and can pull humid air in.
- Dye test for drains. If water near a wall shows dye in the sump, the drain tile is active.
You want proof, not guesses. Good tests save you from fixing the wrong thing and keep the focus on what causes moisture in basement.

Source: ndgroup.com
Seasonal and climate factors that raise risk
Weather shifts change what causes moisture in basement. Plan for the season, not just the symptom.
- Summer humidity. Warm outdoor air hits cool foundation walls and condenses. Avoid venting hot humid air into a cool basement.
- Spring rains and snowmelt. Soil stays saturated. Hydrostatic pressure rises. Window wells flood fast.
- Fall leaf loads. Gutters clog and overflow. Downspouts splash at the wall.
- Winter stack effect. Warm air rises and escapes upstairs. Cold air gets pulled in at the basement, sometimes with damp soil air.
- Coastal and river zones. High water tables and storm surges stress drains.
- Arid climates. Less rain, but swamp coolers and humidifiers can push indoor RH too high.
Match strategies to the season. This is key to solving what causes moisture in basement in a lasting way.
Source: therealsealllc.com
Health and structural risks you should not ignore
Moisture affects more than comfort. It can harm people and your home.
- Mold and microbes. Dampness supports mold and bacteria. Studies link indoor dampness to asthma and allergies.
- Dust mites. Mites thrive at high RH and trigger sniffles and wheeze.
- Wood rot and rust. Joists, sill plates, and fasteners weaken over time.
- Concrete damage. Freeze cycles and salts can cause spalling and cracks.
- Odors and VOCs. Dampness can raise odors from stored items and some finishes.
A dry basement protects air for the whole house. That is why I push clients to find what causes moisture in basement and fix it at the root.

Source: umn.edu
Fixes and prevention: from quick wins to permanent solutions
Start with source control. Then manage air and surfaces. Each fix maps to what causes moisture in basement at your home.
Fast, low-cost steps
- Run a dehumidifier with a drain hose. Target 45 to 55 percent RH. Clean the filter.
- Improve airflow. Open interior doors. Add a small fan for dead corners.
- Insulate cold pipes. Use foam sleeves to stop pipe sweat.
- Store off the floor. Use shelves and leave gaps from walls.
Exterior upgrades that make a big difference
- Clean gutters. Add larger downspouts if needed. Install guards if trees are close.
- Extend downspouts. Aim discharge at least 6 to 10 feet from the wall.
- Regrade soil. Slope away from the foundation by at least 1 inch per foot for several feet.
- Fix window wells. Add covers and drains tied to gravel bases.
- Seal exterior wall penetrations. Use durable sealants at vents and lines.
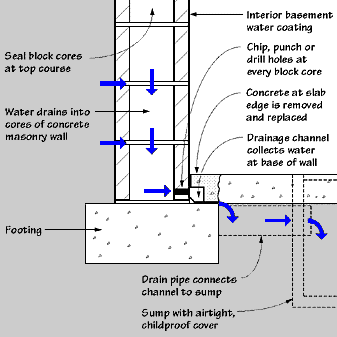
Structural and long-term solutions
- Exterior waterproofing. Apply a membrane and drainage board with a footing drain.
- Interior drain tile with sump pump. Relieves hydrostatic pressure and routes water out.
- Add a backup pump. Battery or water-powered backups handle outages.
- Capillary breaks and vapor barriers. Use polyethylene under slabs and rigid foam on walls before finishing.
- Crack repair. Epoxy or polyurethane injections stop active leaks.
- Insulate foundation walls with rigid foam. This warms surfaces and cuts condensation.
These steps line up with the main drivers of what causes moisture in basement. Fix the source, then condition the space.
DIY tests and tools I trust
I keep a simple kit for fast checks. These tools help confirm what causes moisture in basement without guesswork.
- Digital hygrometer with data logging. Track RH and temperature over days.
- Infrared thermometer. Check surface temps to compare with dew point.
- Moisture meter for wood. Probe joists and sill plates.
- Calcium chloride or RH in-slab tests. Useful before flooring installs.
- Smoke pencil or incense. Find air leaks at rim joists and penetrations.
- Blue painter’s tape and clear plastic. Run the plastic sheet test on walls and floors.
Do not skip safety. Wear gloves and a mask when checking mold or old insulation. Stop if you see signs of structure damage and call a pro.
Source: umn.edu
Cost guide and when to call a pro
Costs vary by home and source. Your price depends on what causes moisture in basement and the fix needed.
Typical ranges I see
- Dehumidifier and pipe insulation. Low hundreds.
- Gutter, downspout, and grading work. A few hundred to a few thousand.
- Window well repair with drains and covers. A few hundred per well.
- Interior drain tile with sump. Several thousand to low five figures based on size.
- Exterior waterproofing with drain. Often five figures due to digging and access.
Call a licensed pro when you see any of these
- Frequent standing water after rain.
- Horizontal cracks or bowing walls.
- Mold over 10 square feet.
- Repeated pump failure or backup.
- A musty smell that returns after basic steps.
A good contractor should give a clear scope that matches what causes moisture in basement at your house, not a generic package.
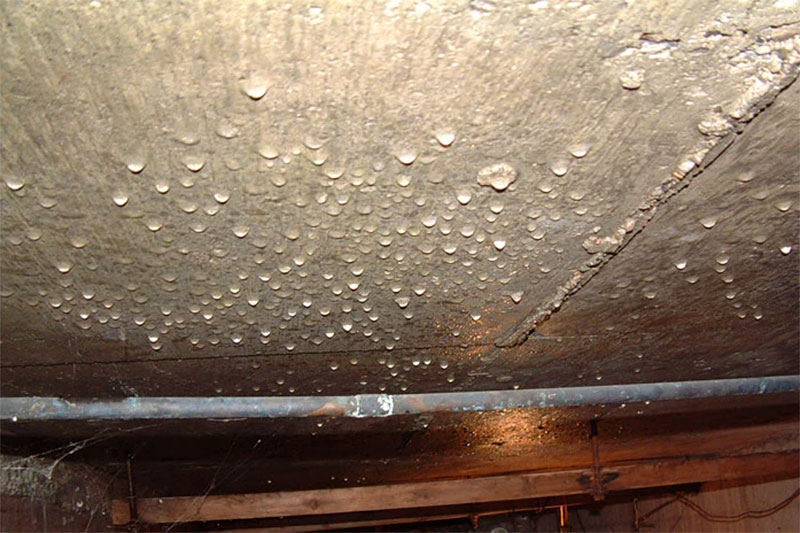

Source: supremebasements.com
Maintenance checklist and habits that keep basements dry
Prevention keeps costs low. Build a simple routine and stick to it.
Monthly
- Check RH and temp. Adjust the dehumidifier if needed.
- Inspect the sump pump and test the float.
- Look for new stains, rust, or musty smells.
Spring and fall
- Clean gutters and extend downspouts.
- Confirm slope away from the house. Add soil where needed.
- Test backup power for the pump.
Before big storms
- Clear window wells and stair drains.
- Lower RH to the mid 40s.
- Move boxes off the floor.
Yearly
- Inspect crack repairs and sealant joints.
- Service AC coils and drain lines.
- Review the basement for any fresh clues of what causes moisture in basement.
These habits keep small issues small. They also give you fast clues if something changes.
Source: umn.edu
Frequently Asked Questions of what causes moisture in basement
What is the most common source of basement moisture?
Poor surface drainage is the top cause. Short downspouts and clogged gutters push water straight to the foundation.
How do I know if it is a leak or condensation?
Do the plastic sheet test on a cool wall or the slab. Water under the plastic points to moisture through concrete, while water on top points to indoor condensation.
Will a dehumidifier fix everything?
No. It helps with air moisture and condensation. It cannot stop liquid water from leaks, ground water, or hydrostatic pressure.
Can I paint the walls to stop moisture?
Paint is not a fix for bulk water. Use coatings only after you manage drainage, cracks, and vapor with proper systems.
When should I worry about health risks?
If RH stays above 60 percent, if you see visible mold, or if breathing issues get worse, act fast. Find the source and lower moisture.
How does climate change what causes moisture in basement?
Humid summers raise condensation risk, while heavy rains raise hydrostatic pressure. Your plan should match your season and local soil.
What causes moisture in basement even in new homes?
New concrete holds water and needs time to dry. Bad grading or downspout design can also affect new builds.
Conclusion
A dry basement starts with a clear diagnosis. Learn what causes moisture in basement at your home, fix the source, and then control air and surfaces. That simple order saves money and stress.
Take one step today. Check gutters, measure humidity, and run the plastic sheet test. If you need more help, reach out to a trusted pro, subscribe for more guides, or leave a comment with your specific setup so I can point you to the right next step.
